Orthopedics is the medical specialty that focuses on the diagnosis, correction, prevention, and treatment of patients with skeletal deformities and injuries. These conditions can involve the muscles, ligaments, joints, bones, and nerves, primarily in the arms, legs, back, and neck. Here are some of the most common orthopedic issues and their treatments.
Osteoarthritis
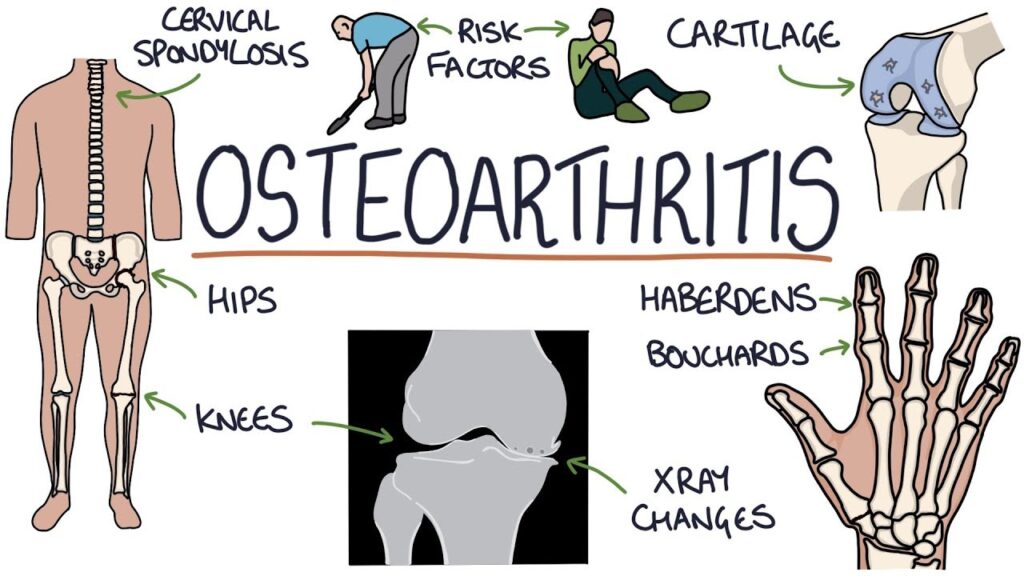
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease and the most common form of arthritis. This condition typically develops gradually over many years, as the cartilage in your joints wears down. This loss of cushioning causes pain, swelling, stiffness, and, in some cases, a decreased range of motion.
Treatment for osteoarthritis often involves a combination of physical therapy, weight management, and medication to manage pain and reduce inflammation. In more severe cases, doctors may recommend joint replacement surgery, such as knee or hip replacements.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Unlike osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissue. This can lead to painful swelling, bone erosion, and joint deformity.
The goal of rheumatoid arthritis treatment is to stop inflammation, relieve symptoms, prevent joint and organ damage, and improve overall well-being. Treatment typically includes medication such as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgery to repair damaged joints.
Osteoporosis
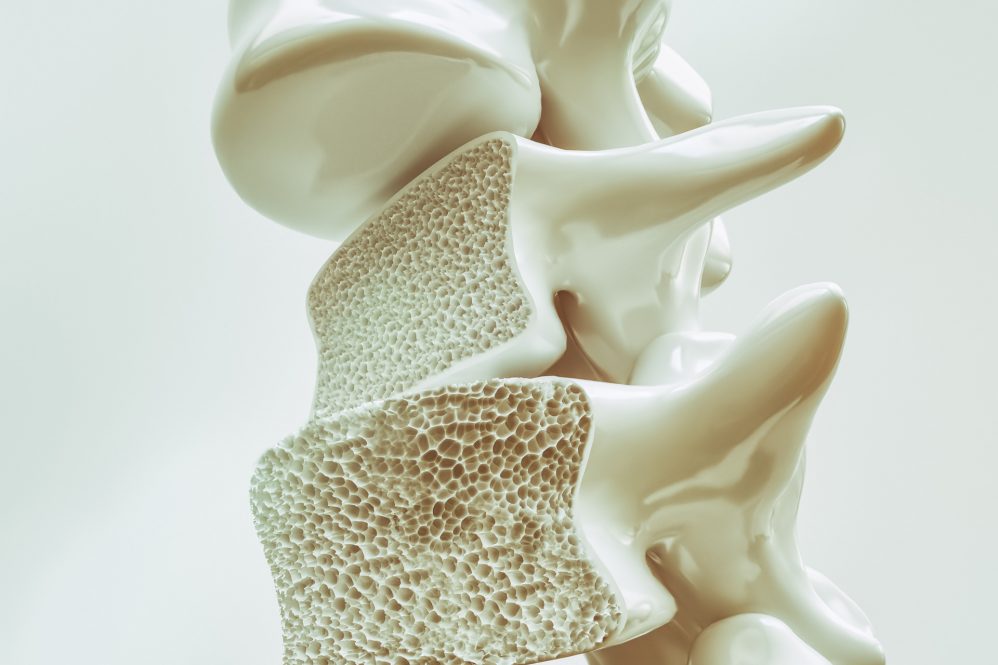
Osteoporosis is a bone disease characterized by weak, brittle bones that are more susceptible to fractures. It occurs when the body loses too much bone or makes too little new bone, or both.
Management of osteoporosis often includes a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. These changes can involve dietary modifications, increased exercise (especially weight-bearing activities), and cessation of harmful habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Medications, such as bisphosphonates, can help slow bone loss.
Rotator Cuff Tear
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint. A tear here is a common cause of pain and disability among adults, often resulting from wear and tear over time or from acute injury.
Non-surgical treatments include rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medication. However, severe tears may require surgical intervention. This can involve arthroscopy, a less invasive procedure, or open surgery for larger or more complex tears.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
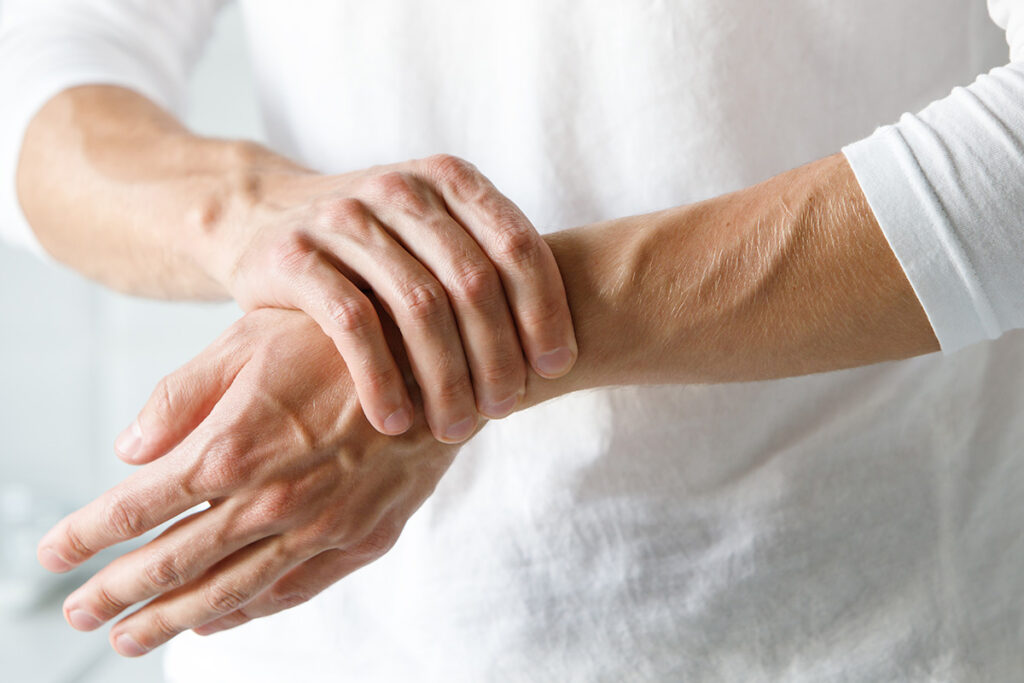
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition caused by pressure on the median nerve in the wrist, often due to repetitive motions like typing. Symptoms can include numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and fingers.
Treatment often starts with non-surgical options like wrist splinting, avoiding activities that worsen symptoms, and taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). In more serious cases, corticosteroids or surgery may be necessary.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tear
An ACL tear is a common knee injury, often seen in athletes. It can cause pain, swelling, and instability, and may limit the range of motion in the knee.
Initial treatment for an ACL tear typically includes rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), along with pain relievers and physical therapy. Depending on the severity of the tear and the patient’s lifestyle, surgery may be needed to restore knee stability.
Plantar Fasciitis
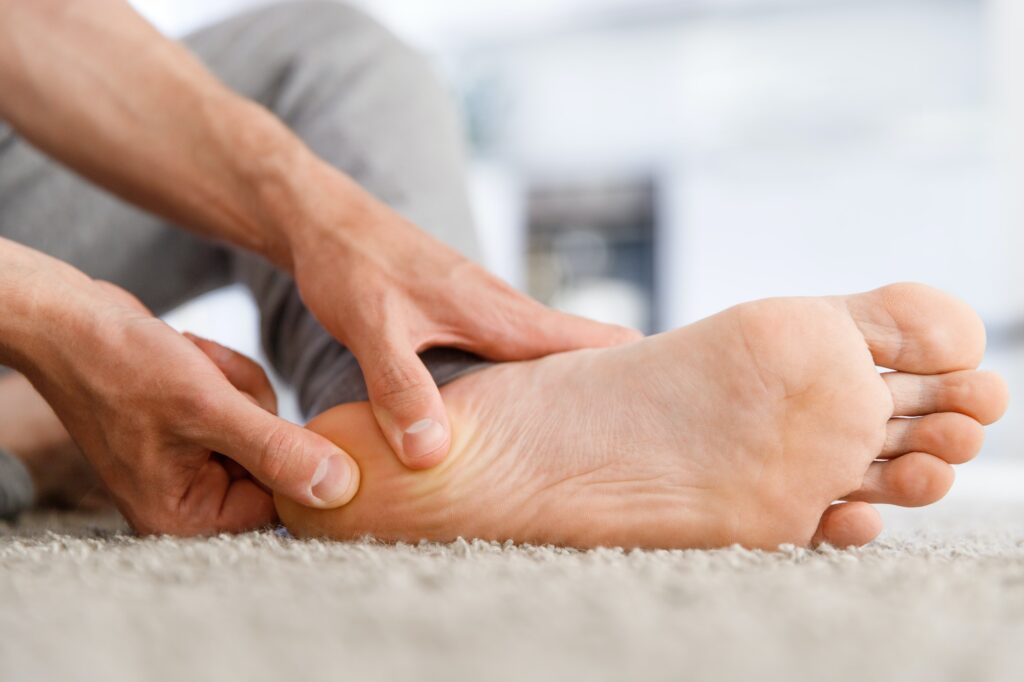

Plantar fasciitis, a common cause of heel pain, occurs when the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue running across the bottom of your foot, becomes inflamed or irritated. This condition is often seen in runners or people who are overweight.
Treatment for plantar fasciitis generally begins with conservative methods such as rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain relievers. Physical therapy can also be beneficial, teaching exercises to stretch and strengthen the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon and to improve stability. If these methods are not effective, your doctor may suggest other treatments, like steroid injections or shock wave therapy.
Sciatica
Sciatica is a condition characterized by pain radiating along the path of the sciatic nerve, which branches from your lower back through your hips and buttocks and down each leg. Sciatica typically affects only one side of your body and is commonly caused by a herniated disk, bone spur on the spine, or narrowing of the spine.
The primary goal of treatment for sciatica is to alleviate pain and increase mobility. This may involve physical therapy and exercises to improve posture, strengthen the muscles that support your back, and improve flexibility. If these are not effective, your doctor may recommend medications or even surgery in severe cases.
Spinal Stenosis
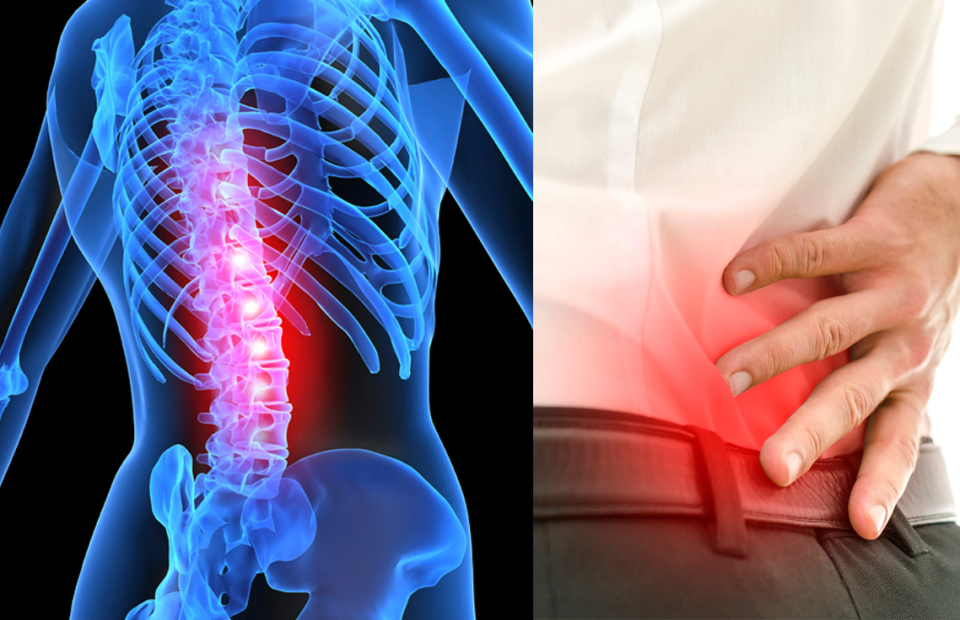
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spaces within your spine, which can put pressure on the nerves that travel through the spine. Most commonly caused by wear-and-tear changes in the spine related to osteoarthritis, it typically occurs in the lower back and neck.
Treatment of spinal stenosis might include medications, physical therapy, steroid injections, or surgery, depending on the severity of symptoms. Lifestyle modifications and alternative therapies such as massage and acupuncture can also be helpful.
Bunions
Bunions are bony bumps that form on the joint at the base of your big toe, causing it to deviate towards the other toes. This common foot deformity can cause discomfort and even pain, especially when wearing shoes or walking.
Conservative treatments for bunions include wearing comfortable shoes with a wide toe box, using bunion pads, and taking pain relievers. Physical therapy exercises may help maintain joint mobility and prevent stiffness. However, if the pain is severe or if mobility is affected, surgical intervention may be necessary to realign the toe.
Tennis Elbow
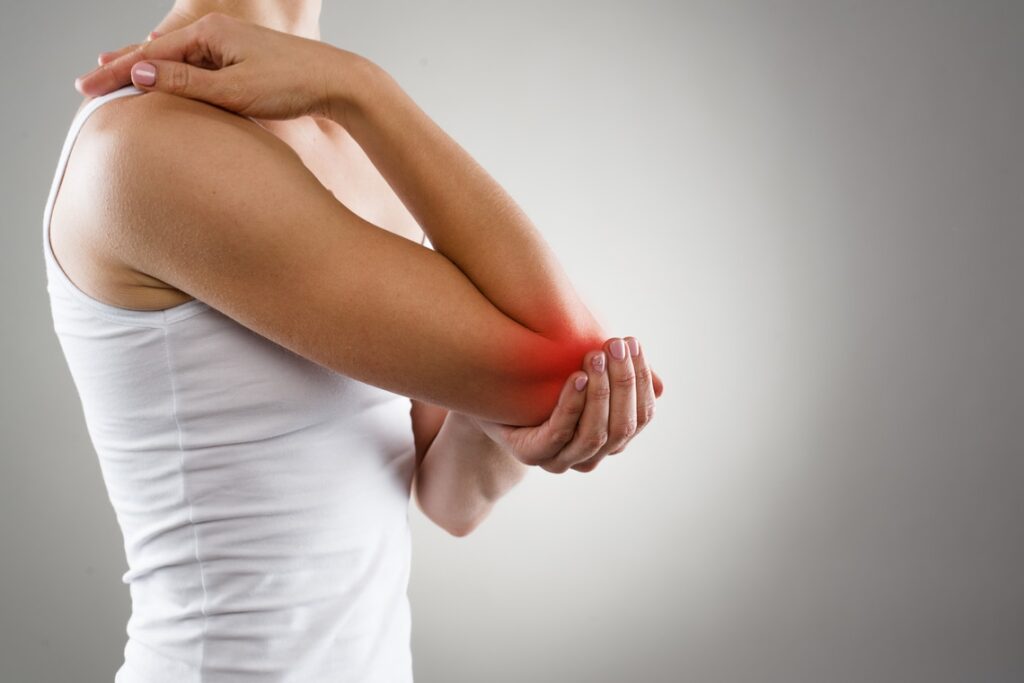
Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is an overuse injury causing pain on the outside of the elbow, often due to repetitive wrist and arm motions. While it’s particularly common in tennis players, it can affect anyone who performs repetitive arm movements.
Treatment typically includes rest, physical therapy, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Steroid injections may also be used for short-term relief. For persistent symptoms, surgery or other procedures like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections may be considered.
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition that causes a sideways curvature of the spine. Most commonly, it develops in the pre-puberty growth spurt and can range from mild to severe.
Mild scoliosis is usually monitored with regular check-ups, and in some cases, physical therapy exercises can help improve strength and flexibility. Moderate to severe scoliosis may require bracing to prevent further curvature. In severe cases, where the curve is more than 45 to 50 degrees, surgery may be recommended.
Orthopedic disorders cover a wide spectrum, each with its unique challenges and treatment approaches. As we’ve explored in this article, treatments can range from conservative measures such as rest, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications, to surgical interventions in more severe cases.
The key to successful treatment often lies in early detection, comprehensive evaluation, and a personalized treatment plan. By consulting an orthopedic specialist, individuals can address their orthopedic health concerns and strive for an active, pain-free life.
While orthopedic disorders are common, advancements in medical knowledge and technology mean that most people can lead a fulfilling life despite these challenges. As research continues, the future of orthopedics promises even more effective strategies for managing these conditions.
 HQ Grande Prairie HQ Grandie Prairie is an online news portal aimed at providing latest day to day happenings of the World to its viewers.
HQ Grande Prairie HQ Grandie Prairie is an online news portal aimed at providing latest day to day happenings of the World to its viewers.